Why Small-Scale Fishers in Indonesia Need More Protection – And How We Can Help
Indonesia is one of the world’s largest producers of octopus, with Sulawesi waters contributing around 50% of the country’s total octopus production. The fishery is predominantly small-scale and artisanal, relying on traditional fishing methods such as handline and spear. Fishers operate small vessels under 1 Gross Tonnage (GT), and in some cases, they do not use vessels at all, instead gleaning for octopus along the shoreline during low tide. This fishery plays a vital role in the livelihoods of coastal communities across Wakatobi, Selayar, Banggai Laut, Luwuk, and Tojo Una-Una Regencies in Sulawesi waters.
Collaborative Efforts for Sustainable Solutions
Although the octopus fishery plays a significant role in Indonesia’s seafood industry, it largely operates informally, posing challenges for many fishers in terms of legal recognition, sustainability, and access to social security. The lack of proper registration and regulatory oversight have hindered opportunities for small-scale fishers to benefit from government support programs and long-term resource management initiatives. Promoting the sustainability of this fishery calls for collaborative efforts among government agencies, NGOs, and local communities to enhance governance, safeguard fishers’ rights, and integrate them into national protection frameworks.
In 2024, Pesisir Lestari (YPL) with the Octopus FIP – Consortium NGOs in Sulawesi – Indonesia conducted Social Responsibility Assessment (SRA) to look into the working conditions of these small-scale fishers. SRA serves as a complement to FIP to determine the extent of social risk in fisheries activities. The assessment identified that while there are no major findings in social risks related to forced labor, child labor, or human trafficking, the sector still faces challenges in terms of outreach and access to social protection. Many fishers operate small, unregistered vessels (under 1 Gross Tonnage), which potentially hamper their ability to obtain official recognition, fisheries subsidies and financial support.
This is certainly in line with the principles of the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency, which emphasizes the importance of clear information and vessel registration as a form of openness and legal assurance for fishers and fisheries actors (Principle 1), and how this can contribute to strengthening their representation in inclusive policy-making processes, including the provision of various forms of support that reinforce the position of fishers, especially small-scale fishers (Principle 9).
“Most fishers understand their basic rights, like the freedom to organize and sell their catch independently. But there are still major gaps in knowledge, many don’t know how to file complaints, register their boats, or access and utilize health and employment insurance provided by the government. We need an approach that goes beyond echoing fishers capacity; one that actively involves fishers in policy planning and decision-making. Strengthening collaboration between fisher groups and the government is the key to ensuring both recognition and empowerment,” stated Faridz Fachri, Program Manager, Pesisir Lestari (YPL).
Small-scale fishers operate in an unpredictable environment, where factors such as adverse weather conditions, fluctuating octopus populations, and market price declines can lead to unstable earnings. Unfortunately, they have limited access to comprehensive social security measures, including informal employment insurance, accident coverage, and pension schemes. While informal community-based support systems exist, there remains a significant need for institutional mechanisms to ensure their long-term security and well-being.
To address these concerns, Pesisir Lestari (YPL) and partners brought together key stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, academics, private sectors and community representatives into a discussion via a webinar event on December, 16th, 2024. The discussions aimed to enhance understanding of the importance of social security for small-scale fishers and explore collaborative solutions to improve their access to safety nets.
 Participants of the Human Rights and Social Responsibility Policy Training, Central Sulawesi
Participants of the Human Rights and Social Responsibility Policy Training, Central Sulawesi
“Actually, we have been working to connect small-scale fishers with the national employment insurance system through BPJS, and the response has been quite positive. However, our coverage remains limited due to the challenging access, given Indonesia’s vast archipelagic geography. Cross-sector collaboration is truly needed,“ said Lili Widodo, Head of Fishers Protection Task Force, Directorate General of Capture Fisheries, MMAF
Key Challenges and Findings
One of the key takeaways from the webinar was the need for a suitable vessel registration process for small fishing fleets. By seizing the process and offering incentives for registration, formally recorded and registered to unlock opportunities (as in line with the Principle 1 and 9 of the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency). Many fishers were perplexed as to where to start the process due to bureaucratic hurdles, thus Pesisir Lestari (YPL) initiated a pivotal step for the fisher community in Luwuk Regency together with local authority to open registration and vessel-measurement booths to provide direct access for fishers. Paralelly, a human rights and social responsibility training was conducted for the fishing communities in Luwuk, Central Sulawesi, to help them navigate the system and take advantage of existing social security programs.
Further, the discussion on webinar highlighted how legal frameworks must be strengthened to accommodate the needs of small-scale fishers, while targeted programs should be designed to facilitate their access to essential social services. Additionally, collaboration with local government and community development programs at the village and district levels will be key to improving fisher resilience and ensuring they are not left behind.
Ensuring social protection for small-scale fishers is not the responsibility of a single entity. It requires coordinated action among policymakers, industry leaders, civil society organizations, and fishers themselves. By working together, stakeholders can create a more resilient and sustainable fisheries sector where small-scale fishers are recognized, protected, and empowered to continue their vital contributions to Indonesia’s economy and food security.
Expert Insight: Bridging the gap between fisheries data transparency and policy transparency
On World Fisheries Day, we sat with Dr Daniel Skerritt, Senior Analyst with the Transparent Oceans Initiative at Oceana and an Affiliated Researcher with the Fisheries Economics Research Unit at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, to untangle some complex concepts of fisheries transparency and hear his broad perspective on the subject.
We all agree that improving fisheries transparency is a crucial, yet daunting task for governments around the world. What is the practical value of open and accurate data about ‘who is fishing where, how, and how much’?
The value of enhancing transparency, particularly related to data disclosure, is incredibly high. When we talk about knowing ‘who is fishing, where, how, and how much,’ we’re addressing the core information that underpins sustainable fisheries management and regulatory compliance.
Knowing who is fishing and ensuring they are properly licensed and monitored is critical for accountability—if rules are broken, we can identify and take appropriate action against the offenders. It also means that we can understand the distribution of access, that is, if the opportunities to catch fish are shared fairly. This helps maintain a level playing field for all stakeholders.
Knowing where they are fishing helps protect sensitive habitats and control the spatial distribution of fishing effort. It is about making sure that fishing doesn’t occur in marine protected areas or in areas reserved for specific communities. It’s also about safety and minimizing conflicts in busy, shared marine spaces.
How fishing is done relates directly to the impact of fishing. Ensuring methods being used are selective, low-impact, and avoid by-catch of non-target species and juvenile fish, is important for the health of ecosystems. And ensuring vessels are properly equipped and maintained is important for crew safety.
Lastly, knowing how much is being caught is fundamental to fisheries management. Accurate catch data are indispensable for setting quotas and ensuring that exploitation stays within ecological limits to prevent overfishing.
Together, this information enables more informed decision-making, which is critical not only for sustainability but also for fostering trust and cooperation among stakeholders, regulators, and the public.
What are the main challenges or barriers to achieving greater transparency in global fisheries, and how can they be addressed?
Key hurdles include the lack of political will or appropriate political processes, particularly in wealthier nations, and technological and financial constraints in low-and middle-income regions.
Often, there’s resistance among actors, including some government bodies, who may benefit from less transparent practices or processes. To address this, building international coalitions that advocate for and support transparency can help align different nations towards common goals, and raise the standard for all fisheries. We need to ensure that our political and governance processes are up to the task of delivering transparency, this includes ensuring that resource users are held to account and that society can democratically hold decision-makers to account!
A significant hurdle may be a lack of financial, institutional, and technological capacity. It is not cheap, nor straightforward to collect and disclose information and therefore different forms of support, such as investment in technology and capacity building can empower governments to develop their own transparency efforts. This also means that we need to be clear about what or where transparency is most needed, who it will benefit, and to what end.
Another challenge is the balance between transparency and its potential unintended consequences, including when transparency clashes with confidentiality, privacy, and data protection rights. For example, a government is not expected to publish stakeholders’ personal information or the patrol patterns of their enforcement vessels.
So, clearly there are limits to transparency, but it is important that we agree where the limit between accountability and excessive privacy lies―the threshold of those limits may be different for different communities―and do not allow this challenge to prevent progress towards effective transparency.
What strategies can be implemented by governments to ensure that transparency of data and information in fisheries translates into transparency in policy-making processes, thus bridging the gap between data transparency and policy transparency?
I think that transparency of data and information in fisheries management is primarily a technical issue, while ensuring this transparency influences policy making is a broader social challenge.
Governments need to establish strong democratic processes that not only involve stakeholders in the policymaking process but enable the people affected by these policies to influence decisions and hold authorities accountable for outcomes. This includes creating legal frameworks that mandate public consultations and stakeholder engagements, ensuring that the voices of those affected by policies—particularly small-scale fishers and coastal communities—are heard and genuinely considered in decision-making.
Furthermore, policy transparency requires that the pathways from data collection to policy formulation are clear and open to scrutiny. This means implementing systems where policy decisions are publicly documented, their justifications linked directly to the data upon which they are based, and that their impact is regularly and transparently evaluated.
Finally, international cooperation plays a vital role. Sharing best practices and successes in integrating data transparency with policy transparency across borders can help raise standards globally.
How can transparency as a tool for ‘good governance’ help deliver measurable improvements in fisheries?
Transparency is the cornerstone of good governance, not just in fisheries! One of the key aspects, as highlighted in my recent paper (Seeking clarity on transparency in fisheries governance and management), is the role of transparency in ensuring that governance and management interventions are not only implemented effectively but also remain adaptable to changing conditions.
Firstly, transparency allows for the regular evaluation of policies. By making information about fisheries management publicly accessible, stakeholders, including the communities most affected by these policies, can see whether the objectives are being met. Openly assessing performance against stated goals enables monitoring and also facilitates informed discussions on the efficacy of different interventions. Moreover, transparency ensures accountability. When decision-makers know their actions and decisions are being observed and scrutinized (and that they will be democratically held to account), it naturally drives them to adhere more closely to the rules and to commit to achieving the best possible outcomes for society. This is particularly critical in fisheries, where biodiversity and the livelihoods of millions of people are at stake.
Additionally, if policies are found lacking, transparency mechanisms facilitate the necessary adjustments. This is not only about exposing failures but about creating a feedback loop where policies can be dynamically refined and improved based on real-world data and stakeholder input.
Ultimately, I think that the goal of transparency in fisheries governance goes beyond IUU fishing and is about creating systems where policies are not only designed well but are also continually optimized to ensure sustainable and equitable use of marine resources. When this does not happen we need to make sure that there are processes in place to hold decision-makers, or rule-breakers to account.
Cover image: © Maisie Pigeon
South Korea to become a global leader in fisheries transparency
The recent amendment of the revised Distant Water Fisheries Development Act by Korea’s Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries demonstrates the country’s strong commitment to sustainable fisheries and transparent seafood supply chains.
Korea’s Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries adopted on 25 October the revised Distant Water Fisheries Development Act that includes improvement of the country’s Catch Documentation Scheme (CDS) – one of the tools designed to curb illegal, unregulated and unreported (IUU) fishing. With this act, Korea fully met the recommended Key Data Elements (KDEs) – the types of data required to trace seafood products successfully through the supply chain – from the previous 35 percent to the recommended 100 percent, representing the most significant progress made by any country in implementing these recommendations. Moreover, this initiative demonstrates the country’s strong commitment to sustainable fisheries and transparent seafood supply chains.
The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency, a global network of nearly 50 civil society organizations that advocate for government adoption of stronger fisheries policies, praised this achievement by Korea that now positions it as the first country in the world to make such significant progress towards accelerating fisheries transparency.
“I commend the Korea’s Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries for taking this bold step to protect its fisheries resources and our shared ocean amid growing concerns about illegal fishing and seafood safety, and I emphasize our strong international support for these measures,” commented Maisie Pigeon, Director of the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency.
The coalition simultaneously called for the Ministry to intensify its leadership in fisheries transparency by expanding the CDS’ coverage and endorsing the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency – a set of 10 transparency policy principles designed to improve fisheries governance, combat illegal fishing, and prevent human rights and labor abuses at sea.
As the host of the upcoming 10th Our Ocean Conference (28-30 April 2025), Korea has a unique opportunity to demonstrate to the world that it can direct the fight against IUU fishing, by endorsing the Global Charter. By adopting the Charter principles into law and practice, Korea could influence and accelerate the adoption of fisheries transparency measures by other key seafood-importing markets like the US, Japan, the UK, and the EU. These actions position Korea as a champion for developing and standardizing the systems to implement the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency.
As a major global seafood importer, Korea has a due responsibility to consumers to ensure that its supply chains are safe, legal, sustainable and ethical. With its excellence in digital technology, Korea is perfectly positioned to develop a digital platform that includes comprehensive information to enhance consumer’s trust, ensure seafood safety and ethical sourcing of the product. Without seafood traceability – the ability to fully trace the product from the point of sale back to its point of origin – consumers run the risk of unknowingly contributing to the destruction of marine environment and human rights and labor abuses, while perpetrators continue to plunder our oceans. On the flip side, strong traceability prevents seafood fraud, where cheaper seafood is sold as more expensive products, misleading consumers in order to increase profits.
By enacting the principles of the Global Charter, Korea can demonstrate its continued and long-term commitment to sustainable fisheries and its willingness to collaborate with the global community in addressing pressing challenges in marine resource management.
Promoting fisheries transparency through an inclusive approach to fisheries management: examples from the Philippines
Aligned with the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as part of the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, and other international agreements, the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency recognizes through Principle 9, the rights to access to information and public participation in decision- making as an essential element for informed policy decisions, and inclusive fisheries management practices. This principle, frames as an essential aspect of fisheries transparency the publication of fisheries management information and the inclusion of diverse stakeholder groups in the decision-making process on fisheries management as follows:
Principle 9: ‘Publish all collected fisheries data and scientific assessments in order to facilitate access to information for small-scale fishers, fish workers, indigenous communities, industry associations, and civil society in developing fisheries rules, regulations, subsidies and fisheries budgets, and decisions on access to fisheries resources. Make these processes, policies, and decisions easily accessible to the public and enforcement agencies.’
Civil society organizations across the world have implemented mechanisms to promote transparency in the fishing sector through access to information and public participation in fisheries management, as put forth in Principle 9 of the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency. Two examples from the Philippines – the Karagatan Patrol and the Virtual Digital Classrooms – showcase the use of technology, public participation, and collaboration with government agencies in an effort to advance fisheries transparency at a national/regional level.
Karagatan Patrol
Development of the platform “Karagatan Patrol” is an example of collaboration among civil society organizations, government agencies, and coastal communities to collect and manage data. Launched as a nationwide campaign by Oceana in the Philippines to stop illegal commercial fishing in municipal waters, this interactive mapping platform is the result of partnership with the League of Municipalities of the Philippines. The Karagatan Patrol helps report cases of illegal fishing in municipal waters, and disseminates information about potential illegal fishing activities or other environmental violations to the local government, security and enforcement agencies, fisherfolk, industry actors, and media.
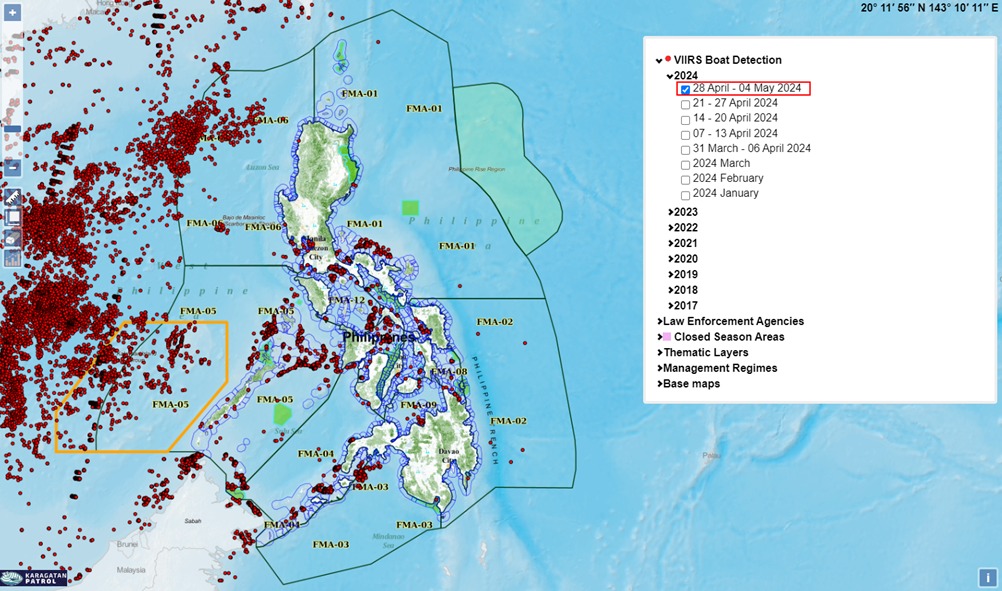
KaragatanPatrol.org
Commercial fishing boat detection maps can be accessed by users to demonstrate possible intrusions of commercial fishing vessels in municipal waters. With data analysis from the map, it’s possible for enforcement authorities to detect incidents in municipal waters and prioritize enforcement efforts to report illegal fishing. Additionally, this platform has a Karagatan Patrol Facebook group and a Twitter account, which allow fisherfolk, officers from Local Government Units, members from law enforcement and regulatory agencies to share information, photos, videos, report violations, and ask assistance from law enforcers to report ongoing illegal fishing.
Virtual Classrooms
In 2021, Oceana’s team in the Philippines launched “virtual classrooms” to share information with fishing communities from different parts of the country, with the objective to actively engage them in the decision-making process and fisheries management efforts. The “Classroom for Fisherfolk” learning series aims to gather information from fisherfolk on the 12 Fisheries Management Areas (FMA) system, established in the Philippines’ territorial sea to promote science-based management and address illegal fishing activities. The classrooms, among other things, voice concerns from fishermen and exchange insights with government officials to jointly deal with the challenges raised.

© Oceana /Chris Jude Orbeta
The examples provided by the Karagatan Patrol and Virtual Classrooms in the Philippines demonstrate the critical role transparency, technology, and inclusive collaboration play in advancing fisheries management efforts. By leveraging digital platforms for information sharing, fostering public engagement, and building partnerships with government agencies and coastal communities, these initiatives highlight best practices that can be replicated and adapted by organizations across the world, offering valuable insights and guidance for promoting transparency and inclusion in fisheries management. Through shared knowledge and collective action, it is possible to ensure the responsible use of marine resources and promote the well-being of coastal communities for generations to come.
Monitoring vessels at sea: a crucial first step to achieving transparency in fisheries
About 75% of global industrial fishing and 25% of other vessel activity is not publicly tracked, asserts the new publication, Satellite mapping reveals extensive industrial activity at sea, issued in Nature with lead authors from Global Fishing Watch – a non-governmental organization that seeks to advance ocean governance through increased transparency of human activity at sea. The findings suggest that these vessels may be at higher risk of participating in illegal fishing activities, like fishing in marine protected areas, or contributing to forced labor or potential human rights abuses.
This also means that our understanding of “who” is fishing “where”, “how” and “in what conditions” the fishing activity occurs, can be limited. As a result, possible negative consequences for coastal communities, marine ecosystems and the global economy are almost impossible to measure.

Over 740 million people depend on the ocean for their livelihoods, nutrition, or both. That creates immense pressure on the ocean, combined with a wide range of harmful human activities that affect its state. Moreover, about a third of fish stocks are fished beyond biologically sustainable levels (threatening the reproduction of fish populations), and an estimated 30–50% of critical marine habitats have been lost owing to human industrialization.
What does public vessel tracking information mean for fisheries transparency?
According to Nature, some of the largest cases of illegal fishing, together with human rights and labor abuses occurring at sea have been committed on vessels that were not using –or required to use- tracking devices. The study revealed that out of the approximately 63,000 vessels detected by GFW between 2017 and 2021, close to a half of them were industrial fishing vessels. Less than 25% of all industrial fishing vessels were publicly tracked, as presented in the following map (adapted from the publication).
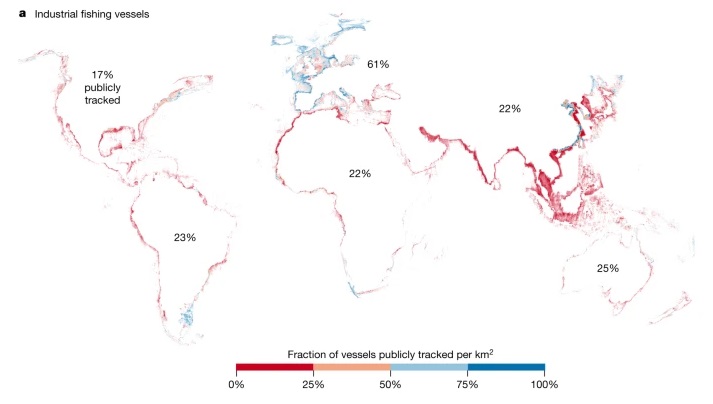
When governments do not require the use of tracking devices for fishing vessels or do not make this information public, their vessels cannot be publicly tracked at the level required to effectively manage fishing activities at sea. For example, this research found fishing vessels not publicly tracked inside protected areas, including Galapagos Marine Reserve (~5 vessels/ week) and Great Barrier Reef Marine Park (~20 vessels/week).
What needs to be done?
The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency (CFT) is a global initiative that brings together civil society organizations to promote transparency in the global seafood sector. The coalition’s work is based on the 10 policy principles included under the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency. One of them – principle five – requires governments to mandate the use of vessel tracking devices and make vessel position data publicly available. Sharing vessel tracking data can help reduce the likelihood of labor rights violations, measure the real impact of fishing activity to effectively manage fish stocks, and detect potential illegal fishing activity within marine protected areas. In 2023, CFT organized a regional workshop in Southeast Asia to learn more about members’ concerns around fisheries transparency, current efforts in the region, and opportunities for possible future collaboration with local organizations. Surprisingly, none of the countries in the Asia region currently makes vessel position data from vessel monitoring system (VMS) publicly available, and while data from Automatic Information System (AIS) is public, most countries do not require the use of AIS for all commercial fishing vessels.
Given the pervasive lack of transparency at sea, CFT calls on governments around the world to make vessel tracking systems a requirement, and its data publicly available to effectively monitor vessel activity at sea.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency?
The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency is a network of international civil society organizations (CSOs) that work towards advancing transparency and accountability in fisheries governance and management. United around the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency, Coalition’s members urge governments around the world to adopt its principles into law and practice. The Charter comprises key transparency priorities in fisheries management that must be addressed in order to combat illegal fishing and overfishing, prevent human rights and labor abuses from happening at sea, ensure strong fisheries management, increase equitable participation in fisheries decision-making, and enable thriving coastal communities.
What does the Coalition aim to achieve?
The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency aims to bring about equitable, sustainable, and well-governed fisheries, free from harmful fishing practices and human rights and labor abuses. We do this by connecting and supporting CSOs in their efforts to advance and accelerate fisheries transparency policies around the world.
Who is part of the Coalition?
Members are at the heart of the initiative as they drive the Coalition’s work by identifying the challenges and priorities to advancing transparency in their countries and/or regions. Members are CSOs around the world that work on fisheries policy reforms. A full list of members can be found on the Members page. Guiding the Coalition is a steering committee of civil society organizations, co-chaired by the Environmental Justice Foundation and Oceana, and joined by Accountability.Fish, Global Fishing Watch, Indonesia Ocean Justice Initiative (IOJI), The Regional Partnership for the Conservation of the Coastal and Marine Zone (PRCM), Seafood Legacy, and the WWF Network. Together, representatives from these organizations provide assistance and share their expertise in fisheries transparency to achieve the Coalition’s mission. The Coalition’s Secretariat supplements members’ efforts through assistance in the areas of communications, research and policy analysis, coordination and partnership building, and strategy development. The Secretariat is composed of a director, policy analyst, communications manager, and associate.
What is the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency?
The Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency is a set of 10 policy principles developed to support CSOs in bringing about effective change in fisheries governance and transparency to combat fisheries mismanagement and illegal fishing, and to prevent human rights and labor abuses from happening at sea. The Charter provides a framework for member organizations to urge governments to implement fisheries transparency policy reforms, in law and in practice. While intended for the entire fisheries sector and readily implementable in industrial fisheries, the Coalition acknowledges that some principles in the Charter require further adaptation before they can be effectively applied to all small-scale fisheries.
How does an organization become a member of the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency?
The Coalition consists of voluntary members. Organizations may request to join the Coalition by submitting a Membership Application form in English, Spanish, or French. The Coalition’s Secretariat will review each application and approve or flag the application for further evaluation by the steering committee. If flagged, the steering committee will discuss the application at their next meeting, with a decision on membership made by consensus. The Coalition will provide a response to new member applications within six weeks of submission. To mitigate any potential conflicts of interest, the Coalition does not extend formal membership to governments, industry entities, or CSOs that operate and/or advocate on behalf of commercial industry. However, these stakeholders are welcome to participate in the Coalition as Affiliates and may request to become an Affiliate by submitting this form.
What are the requirements of membership?
Member expectations and requirements can be found in the Membership Handbook and accompanying Code of Conduct.
Is there a cost for Coalition membership?
There are no membership fees.
Are members financially compensated?
Members are not compensated and should disclose any conflict of interest, including financial or other interest that is adverse to the Coalition’s interests or would otherwise interfere with performance in the Coalition.
Can an organization that does not work on all Charter principles still join the Coalition?
The Coalition does not expect members to work on all Charter principles. However, when joining the Coalition, members agree to the Charter in full as its principles serve as the Coalition’s guiding framework.
How is the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency different from other transparency-focused efforts?
A number of organizations and coalitions are already doing important work to increase fisheries transparency through directly partnering with governments, promoting improved management of regional fisheries management organizations, and working closely with industry to enhance their transparency and traceability practices. The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency is adding to these on-going efforts by centering its approach on organizing CSOs, helping them to accelerate transparency policy reforms through government advocacy. The Coalition’s focus on civil society enables the Coalition to complement the efforts of these other initiatives to collectively move the needle forward on transparency in fisheries globally.
How is the Coalition funded?
The work of the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency is made possible thanks to the generous financial support of Bloomberg Philanthropies, Oceans 5, and Oceankind. The Coalition does not accept funding from industry or government sources.
Civil society groups launch Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency at 2023 Our Ocean conference
The launch of the Charter by the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency lays out a new roadmap to advance marine governance around the world.
PANAMA CITY, Panama, March 02, 2023 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — The Coalition for Fisheries Transparency – a new international community of civil society organizations – today launched the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency. The Charter pinpoints the most essential policy priorities needed to combat fisheries mismanagement, illegal fishing, and human rights abuses at sea. Experts, ministers, and delegates from international organizations and companies around the world discussed the benefits of the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency at Our Ocean Conference in Panama this Thursday and Friday – an annual meeting for countries, civil society and industry to announce significant actions to safeguard the world’s oceans.
“Ghana recognizes the critical role that transparency plays in the fight against illegal fishing to protect livelihoods and provide food security to our coastal communities,” said Hon. Mavis Hawa Koomson, Ghana’s Minister of Fisheries and Aquaculture Development. “With the significant progress Ghana has made in the last year on ending harmful fishing practices that have encouraged illegal fishing in our waters, we are now working towards making greater efforts towards sustaining fisheries transparency in Ghana.”
Prof. Maxine Burkett, Deputy Assistant Secretary for Oceans, Fisheries and Polar Affairs at the U.S. Department of State, highlighted how the U.S. plays a leading role in increasing transparency in global fisheries.
“Last year, President Biden released a National Security Memorandum that recognizes the importance of transparency for combating illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing and associated forced labor abuses,” she said. “By enhancing productive information-sharing, the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency will serve as an important complement to the U.S. government’s activities to end IUU fishing through improving fisheries and ocean governance, increasing enforcement efforts, and raising ambition to end IUU fishing globally.”
Additionally, global partnership initiatives, like the Fisheries Transparency Initiative (FiTI), emphasized the importance of equal, multi-stakeholder collaboration to increase transparency in coastal countries for achieving sustainably managed marine fisheries.
“Given the complexity of fisheries governance, multiple transparency efforts are needed to address the various challenges of unsustainable marine fisheries, such as overfishing, IUU fishing, unequal access to fisheries resources, and unfair benefit sharing,” said Dr. Valeria Merino, Chair of the International Board of the Fisheries Transparency Initiative (FiTI). “The 10 principles of the Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency recognize the need for a comprehensive and coordinated approach to fisheries transparency, and has the potential to support existing global endeavors, such as the FiTI, through a much-needed mobilization of civil society organizations to ensure that marine fishing activities are legal, ethical, and sustainable.”
Finally, the role of the civil society to maximize collective impact to improve transparency has been underlined by Mr. Wakao Hanaoka, Chief Executive Officer of Seafood Legacy (Japan), and a steering committee member of the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency. “Our membership in the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency represents a voice of an international community that allows us to strengthen and amplify our efforts amongst the seafood industry and government towards achieving our goal of making Japan a global leader in environmental sustainability and social responsibility,” he explained.
The Global Charter for Fisheries Transparency lays out a new roadmap to advance marine governance internationally, by providing a set of advocacy principles that are both effective and achievable by all stakeholders involved in fisheries governance and management.
“Continuous advocacy efforts by civil society organizations are critical to improving fisheries governance internationally as well as protecting the ocean and the people who depend on its resources,” commented Maisie Pigeon, Director of the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency. “The Coalition’s mission to deliver an urgent shift towards greater transparency in fisheries will be achieved through supporting our members in developing joint strategies, harmonizing and strengthening efforts, and finally – closing transparency policy gaps in fisheries governance,” she concluded.
Through civil society organizations from around the world, the Coalition for Fisheries Transparency calls on governments to apply the Charter’s principles in legislation and practice.
Press contact: Agata Mrowiec agata@fisheriestransparency.net +34 608 517 552



